VS Code Dev Containers
This page will show you how to set up a local Bitwarden server for development purposes utilizing Visual Studio Code Dev Containers. You can read more about this in the Visual Studio Code Dev Containers documentation.
The Bitwarden server is comprised of several services that can run independently. For a basic development setup, you will need the Admin, Api, and Identity services.
Before you start: make sure you’ve installed the recommended Tools and Libraries. Namely, the following:
- Docker Desktop
- Visual Studio Code
- Azure Data Studio
Clone the repository
-
Clone the Bitwarden Server project:
git clone https://github.com/bitwarden/server.git -
Open a terminal and navigate to the root of the cloned repository.
When first opening the repository in Visual Studio Code, you will be prompted to reopen the folder in a Dev Container. If you have not completed the steps in the Configure Env File section below, the creation of the Dev Container will fail.
Configure Git
-
Configure Git to ignore the Prettier revision:
git config blame.ignoreRevsFile .git-blame-ignore-revs -
(Optional) Set up the pre-commit
dotnet formathook:git config --local core.hooksPath .git-hooksFormatting requires a full build, which may be too slow to do every commit. As an alternative, you can run
dotnet formatfrom the command line when convenient (e.g. before requesting a PR review).
Configure Env File
The Dev Container will automatically load the environment variables from the values in dev/.env.
To get started, copy the example file:
-
cd dev
cp .env.example .env -
Open
.envwith your preferred editor. -
Set the
MSSQL_SA_PASSWORDvariable. This will be the password for your MSSQL database server.
Your MSSQL password must comply with the following password complexity guidelines
- It must be at least eight characters long.
- It must contain characters from three of the following four categories:
- Latin uppercase letters (A through Z)
- Latin lowercase letters (a through z)
- Base 10 digits (0 through 9)
- Non-alphanumeric characters such as: exclamation point (!), dollar sign ($), number sign (#), or percent (%).
- You can change the other variables or use their default values. Save and quit this file.
SQL Server
In order to support ARM based development environments such as the M1 Macs, we use the Azure SQL Edge docker container instead of a normal Microsoft SQL Server container. It behaves mostly identical to a regular SQL Server instance and runs on port 1433.
You can connect to it using Azure Data Studio using the following credentials:
- Server: localhost
- Username: sa
- Password: (the password you set in
dev/.env)
Mailcatcher
The server uses emails for many user interactions. We provide a pre-configured instance of MailCatcher, which catches any outbound email and prevents it from being sent to real email addresses. You can open its web interface at http://localhost:1080.
Configure User Secrets
User secrets
are a method for managing application settings on a per-developer basis. They override the settings
in appSettings.json of each project. Your user secrets file should match the structure of the
appSettings.json file for the settings you intend to override.
We provide a helper script which simplifies setting user secrets for all projects in the server repository.
-
Get a template
secrets.json. We need to get an initial version ofsecrets.json, which you will modify for your own secrets values.- Copy the user secrets file from the shared Development collection into the
devfolder. - If you don't have access to the Development collection, contact our IT Manager to arrange access. Make sure you have first set up a Bitwarden account using your company email address.
- This
secrets.jsonis configured to use the dockerized Azurite and MailCatcher instances and is recommended for this guide.
- Copy the user secrets file from the shared Development collection into the
-
Update
secrets.jsonwith your own values:sqlServer>connectionString: insert your password where indicatedidentityServer>certificateThumbprint: insert your Identity certificate thumbprint from the previous stepdataProtection>certificateThumbprint: insert your Data Protection certificate thumbprint from the previous step
installation>idandkey: request a hosting installation Id and Key and insert them herelicenseDirectory: set this to an empty directory, this is where uploaded license files will be stored.
-
Once you have your
secrets.jsoncomplete, proceed to Starting the Dev Container Environment.
Starting the Dev Container Environment
You are now ready to build and run your development server.
-
Start the Dev Container by opening the Command Palette (Ctrl/Command+Shift+P) and selecting Dev Containers: Reopen in Container:
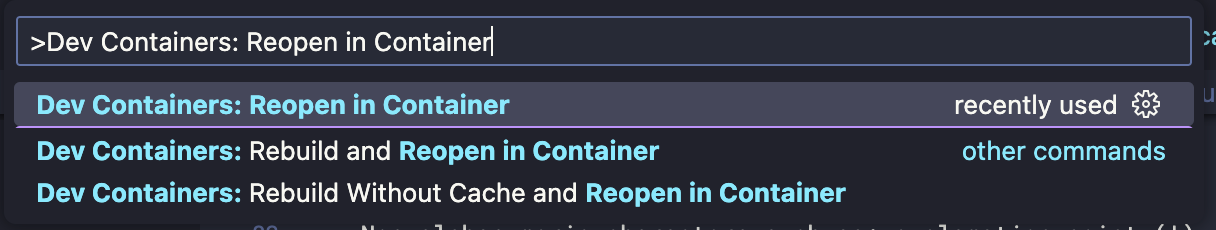
-
Select the appropriate dev container configuration:
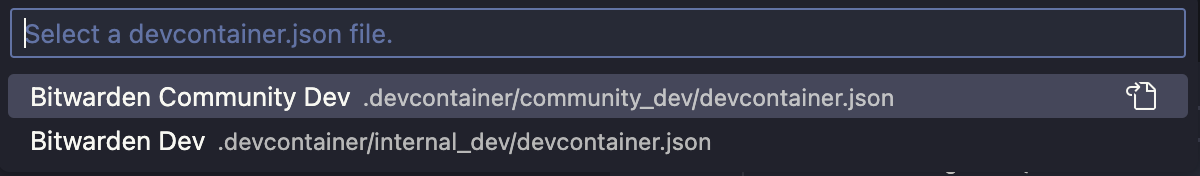
-
Wait for the container to build and start. The first time you open the container, it will take a few minutes to build.
-
Once the container has finished building for the first time, you will be greeted with the
postCreateCommandscript, which will walk you through generating and applying any additional secrets or certificates required for the server to run. -
Follow the on-screen prompts to finish setting up the server. Then, proceed to Build and Run the Server.
Build and Run the Server
You are now ready to build and run your development server.
-
Open a new terminal window in the root of the repository.
-
Restore the nuget packages required for the Identity service:
cd src/Identity
dotnet restore -
Start the Identity service:
dotnet run -
Test that the Identity service is alive by navigating to http://localhost:33656/.well-known/openid-configuration
-
In another terminal window, restore the nuget packages required for the Api service:
cd src/Api
dotnet restore -
Start the Api Service:
dotnet run -
Test that the Api service is alive by navigating to http://localhost:4000/alive
-
Connect a client to your local server by configuring the client’s Api and Identity endpoints. Refer to https://bitwarden.com/help/article/change-client-environment/ and the instructions for each client in the Contributing Documentation.
If you cannot connect to the Api or Identity projects, check the terminal output to confirm the ports they are running on.
We recommend continuing with the Web Vault afterwards, since many administrative operations can only be performed in it.
Debugging
You can use the debugger in Visual Studio Code to debug the server by following these steps:
-
Click the "Debug and Run" button in the left sidebar of Visual Studio Code.
-
Select the desired debug configuration from the dropdown menu.
-
Click the "Start Debugging" button to start the debugger.
Managing and updating the Dev Containers
After you’ve run the deployed the Dev Containers, you can use the
Docker Dashboard or docker CLI to manage your
containers. You should see your containers running under the bitwarden_common group.
Changing the DB Password
Changing MSSQL_SA_PASSWORD variable after first running the Dev Containers will require a
re-creation of the storage volume.
The following will delete your development database.
To do this, stop any running server processes and run the following commands from the
./.devcontainer/bitwarden_common directory:
docker compose down
docker volume rm bitwarden_common-bitwarden_mssql-1
After destroying the DB volume, you can rebuild the Dev Containers in Visual Studio Code and the database using the VS Code Command Palette (Ctrl/Command+Shift+P) and selecting Dev Containers: Rebuild Container.